What You Need to Know: DM1 and DM2 Diagnostic Messaging
The Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) developed the J1939 protocol to standardize communication and diagnostics in heavy-duty vehicles, ensuring interoperability between different electric control units (ECUs) and systems. A crucial aspect of the SAE J1939 protocol is its diagnostic messaging, especially DM1 and DM2 messages, which play a vital role in diagnosing and troubleshooting issues within a vehicle’s network. Additionally, diagnostic messaging in SAE J1939 provides a structured way for electronic control units (ECUs) within a vehicle to exchange diagnostic information, detect faults, and report errors. These messages help technicians identify and address issues, contributing to efficient maintenance and repair process.
DM1 Diagnostic Messages
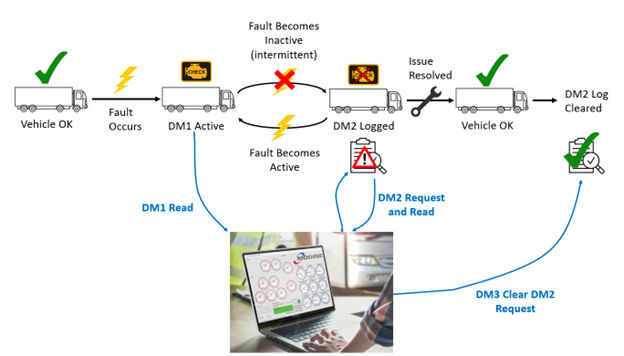
DM1 messages are part of SAE J1939 diagnostic messaging protocol defined in J1939-73 and serve as a comprehensive means of conveying diagnostic information. They primarily focus on active fault codes, which indicate current issues or malfunctions within the vehicle’s systems. DM1 messages are broadcasted by the source ECU to the entire network and can be received and processed by other ECUs.
There are main 5 key components of DM1 Messages:
- Suspect Parameter Number (SPN): The SPN is a unique identifier for a specific fault code. It indicates the type of fault or issue that has been detected. SPNs are standardized and defined in the SAE J1939 documentation
- Failure Mode Identifier (FMI): The FMI provides additional context about the nature of the fault. It describes the severity and the specific problem associated with the fault code indicated by the SPN.
- Occurrence Count: This field indicates how many times the specific fault has occurred since the last clearing of the fault memory.
- SPN Conversion Method: Specifies how the SPN should be converted to a diagnostic trouble code (DTC) for display and analysis.
- Lamp Status Indicators: Provides valuable insights into the vehicle’s condition, offering at-a-glance information about various aspects, including Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL), Red Stop Lamp, Amber Warning Lamp, and Protect Lamp.
DM2 Diagnostic Messages
While DM1 messages focus on active fault codes, DM2 messages are used to communicate previously active or historical fault codes. These codes have been resolved or are no longer active but are retained in the ECU’s memory for diagnostic purposes. DM2 messages also include information about cleared faults, aiding technicians in understanding the vehicle’s history and providing insights into recurring issues.
There are 3 main components of DM2 Message:
- SPN: Similar to DM1 messages, the SPN field in DM2 messages indicates the specific fault code that was previously active.
- FMI: Provides the failure mode information associated with the historical fault.
- Occurrence Count: Indicates the number of times the fault occurred before being cleared.
After the technician reads the previously active fault via DM2 and takes remedial action, the fault history may then be cleared by issuing a DM3 command to the ECU.
Benefits and Applications of DM1 and DM2 Diagnostic Messages
The DM1 and DM2 diagnostic messaging system in SAE J1939 offers a range of benefits and applications across diverse contexts:
- Development and Testing: During the development and testing phase of vehicle systems, DM1 and DM2 messages assist engineers in detecting and rectifying issues before vehicles reach the market.
- Production Support: Applications that have sufficient DM1 fault coverage of all possible faults can use DM1 messages to quickly determine that the vehicle or sub-system build was successful at the end of the production line.
- Maintenance and Repairs: Technicians can use DM1 messages to quickly identify active faults and address them promptly, minimizing vehicle downtime and reducing repair costs. DM2 messages provide valuable historical data that aids in diagnosing recurring issues.
- Fleet Management: Fleet operators can analyze diagnostic data to track the health of their vehicles, schedule maintenance proactively, and optimize fleet efficiency.
- Emissions Compliance: The MIL field in DM1 messages helps identify emissions-related faults, allowing timely corrective actions to maintain compliance with emissions regulations.
Modine EVantage™ Diagnostic and Software and Thermal Management Products: Taking DM1 and DM2 Diagnostics to the Next Level
For a seamless and efficient diagnostic experience, consider leveraging Modine EVantage™ Software’s advanced solutions. Modine EVantage Software provides the ability to download and analyze DM1 and DM2 messages, empowering technicians and fleet managers with deeper insights into vehicle health. This functionally not only works with all EVantage products, but it can also be used to monitor the fault status on any other vehicle node that supports DM1 and DM2 messaging. With Modine EVantage Software, maintenance processes can be streamlined, decisions can be informed, and vehicle fleet performance can be optimized. Explore the capabilities of Modine EVantage Software here and elevate diagnostic practices to new heights.
In the world of heavy-duty vehicles and machinery, SAE J1939 diagnostic messaging, encompassing DM1 and DM2 messages, serves as a cornerstone for effective fault detection, diagnosis, and maintenance. These messages enable swift identification and resolution of issues, contribute to fleet management strategies, support compliance with emissions regulations, and now, with Modine EVantage Software, provide enhanced diagnostic capabilities. By understanding the components, benefits, and applications of DM1 and DM2 diagnostic messaging and exploring Modine EVantage Software’s offerings, vehicle manufacturers, technicians, and operators can harness their power to ensure the optimal performance and longevity of their vehicles.





